Setting up Webhooks
Learn how to configure and use webhooks to receive real-time updates from Koard's payment platform.
Koard allows you to add URLs that receive POST requests when specific events occur in your payment system. Each endpoint can be configured to receive a specific set of events, enabling real-time integration with your applications.
What you learn
In this guide, you'll learn:
- How to set up webhook endpoints in Koard
- How to configure event subscriptions and filters
- How to test and verify webhook functionality
- How to monitor webhook delivery and troubleshoot issues
- Best practices for webhook security and reliability
Before you begin
This guide covers webhook configuration and management in Koard. For a better understanding of available events, see our Available Events guide. If you're ready to start processing payments, see our Running Payments guide.
What are Webhooks?
Webhooks are HTTP callbacks that Koard sends to your application when specific events occur. This allows you to receive real-time notifications about payment events, transaction updates, and other important changes without constantly polling our APIs.
Key benefits:
- Real-time Updates: Get instant notifications about payment events
- Automated Processing: Trigger automated workflows based on events
- Reduced Polling: Eliminate the need to constantly poll for updates
- Better User Experience: Provide immediate feedback to users
Setting Up Webhook Endpoints
Access the Developer Portal
To set up a new webhook endpoint, navigate to one of the following URLs based on your environment:
| Environment | URL |
|---|---|
| UAT | https://app.uat.koard.com/developer |
| Production | https://app.koard.com/developer |
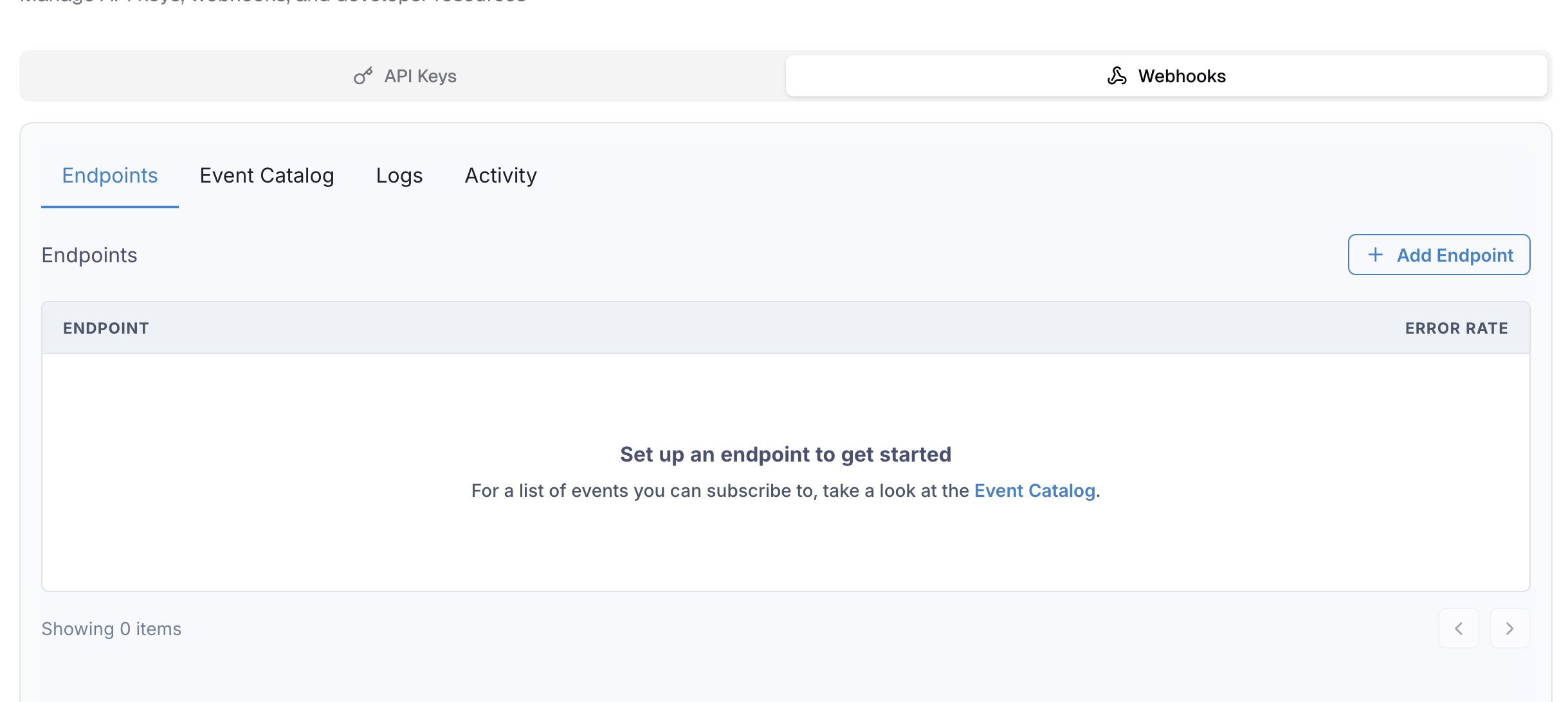
Create a New Endpoint
- Navigate to Add Endpoint: Click "Add Endpoint" on the right side of the developer portal page
- Configure HTTPS Endpoint: Enter your HTTPS endpoint URL that will receive POST requests
- Select Events: Choose which events you want to subscribe to
- Save Configuration: Complete the setup process

Important: Currently, webhooks can only be managed via the Portal, but API management is on the roadmap for creating and managing endpoints and event filters.
Webhook Endpoint Requirements
Your webhook endpoint must meet these requirements:
- HTTPS Only: All webhook endpoints must use HTTPS
- POST Method: Endpoints must accept POST requests
- JSON Payload: Events are sent as JSON in the request body
- Quick Response: Return a 2xx status code quickly (within 30 seconds)
Webhook Configuration
Event Selection
Choose which events you want to receive based on your integration needs. If you don't specify any event types, by default your endpoint will receive all events, regardless of type. This can be helpful for getting started and testing, but we recommend selecting specific events for production.
| Event Category | Description | Common Events |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Events | Transaction lifecycle events | transaction.created, transaction.authorized, transaction.captured, transaction.refunded, transaction.reversed, transaction.settled |
| Account Events | Account management events | account.created, account.updated, account.deleted, account.restored |
| Terminal Events | Terminal configuration events | terminal.created, terminal.updated, terminal.deleted |
| Location Events | Location management events | location.created, location.updated, location.deleted |
| Batch Events | Batch processing and settlement | batch.created, batch.completed |
| API Key Events | API key management events | apikey.created, apikey.revoked |
For a complete list of available events with schemas and examples, see our Available Events guide.
Webhook Headers
Koard uses industry-standard webhook headers powered by Svix for maximum compatibility:
Content-Type: application/json
svix-id: msg_p5jXN8AQM9LWM0D4loKWxJek
svix-timestamp: 1614265330
svix-signature: v1,g0hM9SsE+OTPJTGt/tmIKtSyZlE3uFJELVlNIOLJ1OE=
User-Agent: Svix-Webhooks/1.0
Header Descriptions:
svix-id: Unique message identifier for idempotencysvix-timestamp: Unix timestamp when the webhook was sent (for replay attack prevention)svix-signature: HMAC signature for verifying webhook authenticityContent-Type: Alwaysapplication/json
Retry Policy
Koard implements a robust retry policy with exponential backoff for failed webhook deliveries:
| Retry Attempt | Delay | Time from First Attempt |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | Immediate | 0 seconds |
| 2nd | 5 seconds | 5 seconds |
| 3rd | 5 minutes | ~5 minutes |
| 4th | 30 minutes | ~35 minutes |
| 5th | 2 hours | ~2 hours 35 minutes |
| 6th | 5 hours | ~7 hours 35 minutes |
| 7th | 10 hours | ~17 hours 35 minutes |
| 8th | 10 hours | ~27 hours 35 minutes |
Key Points:
- Response Timeout: 15 seconds per attempt
- Success Criteria: 2xx status code (200-299) indicates success
- Failure Criteria: Any other status code or timeout triggers a retry
- Endpoint Disabling: After 5 days of consecutive failures, endpoints are automatically disabled
- Manual Recovery: Use the dashboard to recover or resend failed messages
Note: When responding to webhooks, return a 2xx status code quickly. Process complex workflows asynchronously to avoid timeouts.
Testing Your Webhook
Create a Test Endpoint
To test your webhook submission, create a webhook that can accept all transaction events and use the Koard SDK to process some transactions:
// Express.js example webhook endpoint
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
app.post('/webhooks/koard', (req, res) => {
const payload = req.body;
const headers = {
'svix-id': req.headers['svix-id'],
'svix-timestamp': req.headers['svix-timestamp'],
'svix-signature': req.headers['svix-signature']
};
try {
// Verify webhook signature using Svix library
const wh = new Webhook(process.env.KOARD_WEBHOOK_SECRET);
const verifiedPayload = wh.verify(JSON.stringify(payload), headers);
// Process webhook after verification
processWebhook(verifiedPayload);
res.status(200).send('OK');
plaintext
} catch (err) {
console.error('Webhook verification failed:', err);
res.status(400).send('Invalid signature');
}
});
function processWebhook(payload) {
const { event, data } = payload;
// Handle different event types
switch (event) {
case 'transaction.created':
handleTransactionCreated(data);
break;
case 'transaction.captured':
handleTransactionCaptured(data);
break;
// Add more event handlers
default:
console.log('Unhandled event:', event);
}
}
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Webhook endpoint listening on port 3000');
});
Test with Koard SDK
Use the Koard SDK to process transactions and trigger webhook events:
// iOS SDK example
import KoardMerchantSDK
// Process a test transaction
let paymentRequest = PaymentRequest(
amount: 1000, // $10.00
currency: .USD,
description: "Test webhook transaction"
)
KoardMerchantSDK.shared.processPayment(paymentRequest) { result in
switch result {
case .success(let response):
print("Payment successful: (response.transactionId)")
// This will trigger webhook events
case .failure(let error):
print("Payment failed: (error)")
}
}
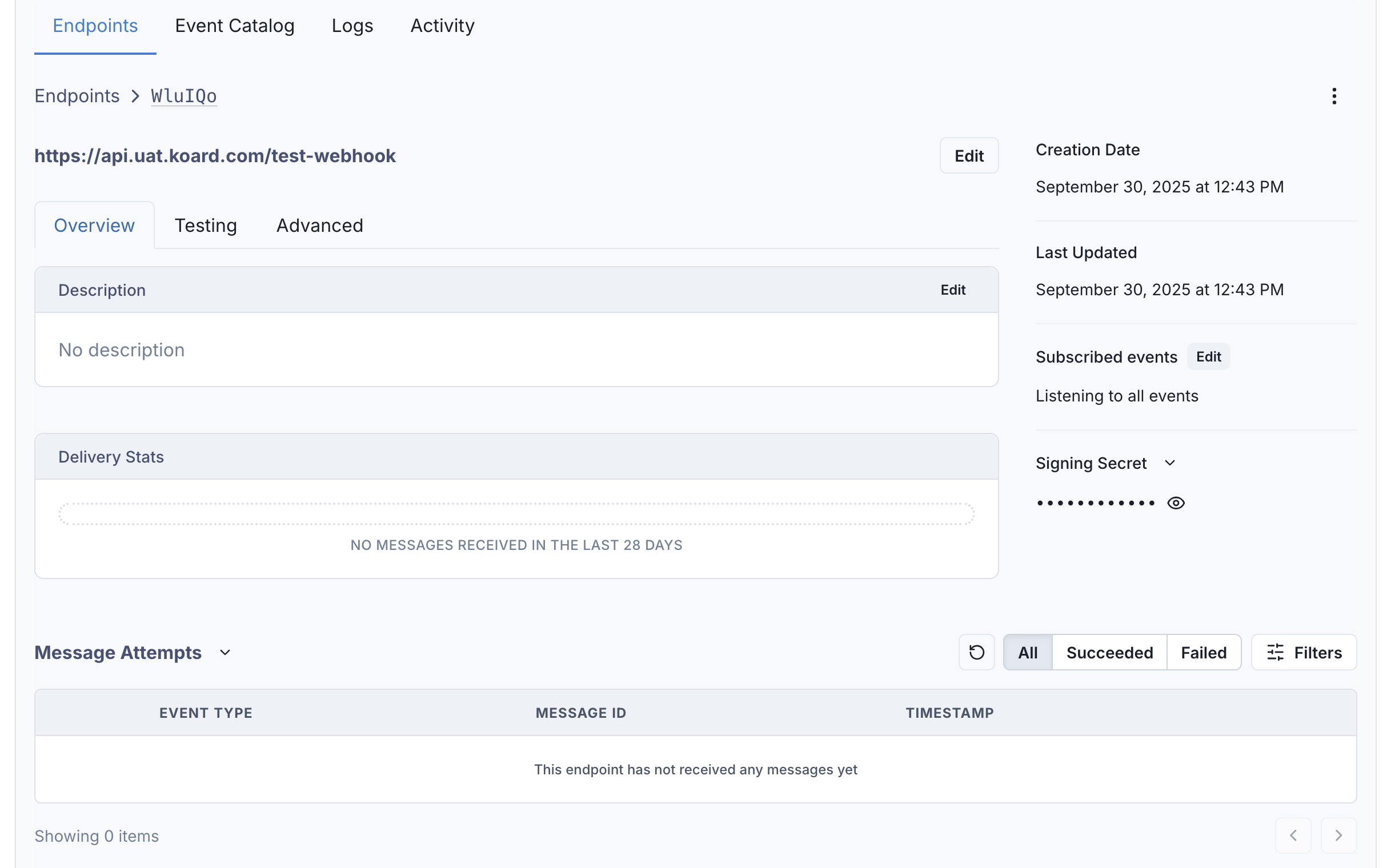
Webhook Security
Signature Verification
Why Verify Webhooks?
Webhook signatures let you verify that webhook messages are actually sent by Koard and not a malicious actor. This prevents:
- Spoofing Attacks: Malicious actors sending fake webhooks
- Replay Attacks: Old webhooks being resent
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Webhooks being intercepted and modified
For a detailed explanation, see why you should verify webhooks.
Using Svix Libraries (Recommended)
Koard uses Svix for webhook delivery, which provides official libraries for easy verification:
Node.js:
const { Webhook } = require("svix");
const secret = process.env.KOARD_WEBHOOK_SECRET; // Get from Koard dashboard
app.post('/webhooks/koard', (req, res) => {
const payload = JSON.stringify(req.body);
const headers = {
'svix-id': req.headers['svix-id'],
'svix-timestamp': req.headers['svix-timestamp'],
'svix-signature': req.headers['svix-signature']
};
try {
const wh = new Webhook(secret);
const verifiedPayload = wh.verify(payload, headers);
// Webhook is verified - process it
processWebhook(verifiedPayload);
res.status(200).json({ success: true });
plaintext
} catch (err) {
console.error('Webhook verification failed:', err.message);
res.status(400).json({ error: 'Invalid signature' });
}
});
Python:
from svix.webhooks import Webhook
import os
webhook_secret = os.environ['KOARD_WEBHOOK_SECRET']
@app.route('/webhooks/koard', methods=['POST'])
def webhook_handler():
payload = request.get_data()
headers = {
'svix-id': request.headers.get('svix-id'),
'svix-timestamp': request.headers.get('svix-timestamp'),
'svix-signature': request.headers.get('svix-signature')
}
try:
wh = Webhook(webhook_secret)
msg = wh.verify(payload, headers)
# Webhook is verified - process it
process_webhook(msg)
return jsonify({'success': True}), 200
except Exception as e:
print(f'Webhook verification failed: {e}')
return jsonify({'error': 'Invalid signature'}), 400
plaintext
Go:
import (
svix "github.com/svix/svix-webhooks/go"
)
func webhookHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
webhookSecret := os.Getenv("KOARD_WEBHOOK_SECRET")
payload, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(r.Body)
headers := http.Header{}
headers.Set("svix-id", r.Header.Get("svix-id"))
headers.Set("svix-timestamp", r.Header.Get("svix-timestamp"))
headers.Set("svix-signature", r.Header.Get("svix-signature"))
wh, _ := svix.NewWebhook(webhookSecret)
err := wh.Verify(payload, headers)
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
// Webhook is verified - process it
processWebhook(payload)
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
plaintext
}
For more examples in other languages (Ruby, PHP, Java, Rust, Kotlin, C#), see the Svix webhook verification documentation.
Manual Verification (Advanced)
If you prefer to verify signatures manually without using the Svix library:
const crypto = require('crypto');
function verifyWebhookSignature(payload, headers, secret) {
const timestamp = headers['svix-timestamp'];
const signature = headers['svix-signature'];
const msgId = headers['svix-id'];
// Check timestamp to prevent replay attacks (optional but recommended)
const timestampSeconds = parseInt(timestamp);
const now = Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000);
if (Math.abs(now - timestampSeconds) > 300) { // 5 minute tolerance
throw new Error('Webhook timestamp too old');
}
// Create the signed content
const signedContent = ${msgId}.${timestamp}.${payload};
// Compute expected signature
const expectedSignature = crypto
.createHmac('sha256', secret)
.update(signedContent, 'utf8')
.digest('base64');
// Extract signature from header (format: "v1,signature")
const signatureParts = signature.split(',');
const headerSignature = signatureParts[1];
// Compare signatures
return crypto.timingSafeEqual(
Buffer.from(headerSignature),
Buffer.from(expectedSignature)
);
}
Important: Use the raw payload body for verification, not the parsed JSON. Different JSON parsers may produce different string representations.
HTTPS Requirements
- HTTPS Only: Webhook endpoints must use HTTPS
- Valid SSL Certificates: SSL certificates must be valid and trusted
- No Self-Signed Certificates: Self-signed certificates are not allowed
- TLS 1.2+: Minimum TLS version 1.2 required
Security Best Practices
- Verify Signatures: Always verify webhook signatures
- Use HTTPS: Only accept webhooks over HTTPS
- Validate Payloads: Validate webhook payloads before processing
- Rate Limiting: Implement rate limiting to prevent abuse
- Logging: Log all webhook events for debugging and security
Monitoring and Logging
Webhook Logs
All webhooks come with detailed logging around deliverability, attempts, and activity history:
- Access Logs: Go to the Logs tab in the developer portal
- Filter Events: Filter by event type and message content
- View Details: Click on individual events to see delivery details
- Monitor Status: Track delivery status and retry attempts
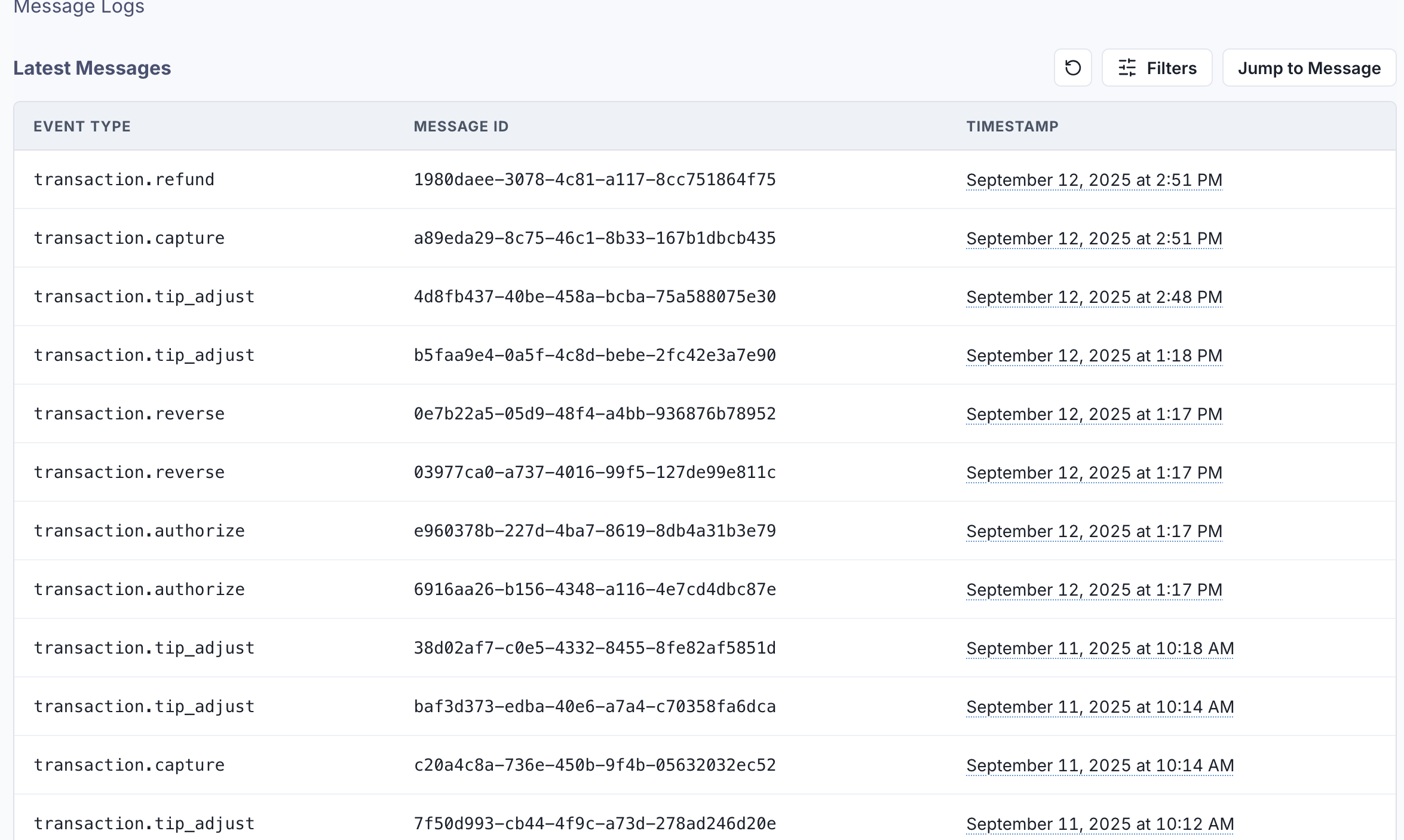
Delivery Status
Monitor webhook delivery status:
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| Delivered | Webhook successfully delivered and acknowledged |
| Pending | Webhook delivery in progress or scheduled for retry |
| Failed | Webhook delivery failed after all retry attempts |
Troubleshooting
Common webhook issues and solutions:
Not Using the Raw Payload Body
This is the most common issue. When generating the signed content, Koard uses the raw string body of the message payload. If you convert JSON payloads into strings using methods like JSON.stringify(), different implementations may produce different string representations, leading to verification failures.
Solution: Use the raw request body exactly as received. In Express.js: use express.raw() or access req.body before JSON parsing.
Missing or Wrong Secret Key
Using an incorrect or outdated webhook secret will cause all verifications to fail.
Solution: Get your webhook secret from the Koard Developer Portal. Remember that secrets are unique to each endpoint.
Timestamp Too Old
Webhooks with timestamps older than 5 minutes are rejected to prevent replay attacks.
Solution: Ensure your server's system time is synchronized (use NTP).
Sending Wrong Response Codes
When Koard receives a 2xx status code (200-299), it's interpreted as successful delivery, even if your response payload indicates a failure.
Solution: Return appropriate status codes:
200for successful processing400-499for client errors (will not retry)500-599for server errors (will retry)
Response Timeouts
Webhooks that don't respond within 15 seconds are considered failed and will be retried.
Solution: Respond immediately with 200 OK and process webhooks asynchronously:
app.post('/webhooks/koard', async (req, res) => {
// Verify signature
const wh = new Webhook(secret);
const payload = wh.verify(req.body, req.headers);
// Respond immediately
res.status(200).send('OK');
// Process asynchronously
queue.add('process-webhook', payload);
});
Failure Recovery
Re-enable a Disabled Endpoint
If all attempts to a specific endpoint fail for 5 days, the endpoint will be automatically disabled.
To re-enable:
- Go to the Koard Developer Portal
- Navigate to Webhooks
- Find the disabled endpoint
- Click "Enable Endpoint"
Recovering Failed Messages
Single Message Recovery:
- Find the message in the Developer Portal
- Click the options menu next to the attempt
- Click "Resend" to retry delivery
Bulk Message Recovery:
- Go to the endpoint details page
- Click "Options" → "Recover Failed Messages"
- Choose a time window to recover from
- All failed messages in that window will be resent
Recovery from Specific Timestamp:
- Find any message near your desired recovery point
- Click the options menu on that message
- Select "Replay all failed messages since this time"
Best Practices
Endpoint Design
- Quick Response: Return 2xx status codes quickly (within 15 seconds)
- Respond First, Process Later: Acknowledge receipt immediately, then process asynchronously
- Disable CSRF Protection: Disable CSRF checks for webhook endpoints
- Use Raw Body: Access raw request body for signature verification
- Error Handling: Implement proper error handling and logging
Event Processing - Idempotency
Why Idempotency Matters:
Webhooks may be delivered more than once due to network issues, retries, or recovery operations. Your endpoint must handle duplicate events gracefully.
Implementation:
Use the svix-id header (message ID) to track processed events:
const processedEvents = new Set(); // In production, use a database
app.post('/webhooks/koard', (req, res) => {
const messageId = req.headers['svix-id'];
// Check if we've already processed this event
if (processedEvents.has(messageId)) {
console.log('Duplicate event ignored:', messageId);
return res.status(200).send('OK'); // Return success for duplicates
}
// Verify and process webhook
const wh = new Webhook(secret);
const payload = wh.verify(req.body, req.headers);
// Mark as processed BEFORE processing to prevent race conditions
processedEvents.add(messageId);
// Process the webhook
processWebhook(payload);
res.status(200).send('OK');
});
Best Practices:
- Store message IDs in a database (Redis, PostgreSQL, etc.)
- Set expiration on stored IDs (e.g., 7 days) to prevent infinite growth
- Use database transactions to ensure idempotency
- Return
200 OKfor duplicate events (they're already processed)
Event Ordering
Important: Don't rely on webhook delivery order. Events may arrive out of sequence due to network conditions, retries, or processing delays.
Solution: Use timestamps from the event payload to determine the correct order:
function processWebhook(payload) {
const { event, data } = payload;
const eventTimestamp = data.created_at; // Unix timestamp
// Get the latest known state
const currentState = database.getTransaction(data.transaction_id);
// Only process if this event is newer
if (!currentState || eventTimestamp > currentState.last_updated) {
// Process the event
updateTransaction(data);
} else {
console.log('Ignoring out-of-order event');
}
}
Security
- Always Verify Signatures: Never skip signature verification in production
- Use Svix Libraries: Use official Svix libraries for proper verification
- HTTPS Only: Use HTTPS for all webhook endpoints (required by Koard)
- Validate Timestamps: Reject webhooks with old timestamps (>5 minutes)
- Secret Management: Securely store webhook secrets (use environment variables)
- Rotate Secrets: Periodically rotate webhook secrets
- Monitor Failures: Alert on repeated verification failures (potential attack)
Monitoring and Alerting
- Track Delivery: Monitor webhook delivery success rates
- Set Up Alerts: Alert on repeated failures or timeouts
- Log Everything: Log all webhook events for debugging
- Monitor Processing Time: Ensure webhooks process within timeout
- Dashboard Review: Regularly review webhook logs in Koard Developer Portal
See also
This wraps up the webhook setup guide. See the links below for related information:
- Available Events - Complete list of webhook events
- Running Payments - Payment processing fundamentals
- Batch and Settlements - Batch processing overview
- Getting Started - Koard platform introduction
